20 Different Types of Screws with Grade 8.8 Properties and DIN/ISO Standards for Industrial Use
20 Different Types of Screws: A Comprehensive Guide for Industrial and Commercial Use
When it comes to fasteners, choosing the correct type of screw can make a critical difference in performance, safety, and efficiency. In industrial manufacturing and construction, each screw type serves a specific purpose, from securing wood to joining heavy-duty metal parts. As a professional manufacturer and supplier, TAIMING emphasizes the importance of understanding screw types, specifications, and standards to ensure compatibility and reliability in various applications.
We first need to understand the drive of the screw
1.Phillips
2.Phillips/slot
3.Phillips/square
4.Hexagon
5.Six-lobe
6.Pozidriv
7.Slotted
8.Six-lobe/slot
9.Six-lobe tamper
10.H-Type
11.Triangle
12.Square
13.Y-type
14.S-type

Different screw slots and their corresponding tools and application scenarios, for example:
Slotted
Corresponding tool: Slotted screwdriver
Features: simple structure, low cost
Application scenarios: traditional furniture, electrical appliances, less frequently used in maintenance
Phillips
Corresponding tool: Phillips screwdriver
Features: can be automatically centered to avoid slipping
Application scenarios: electronic products, household appliances, furniture assembly
Hex socket / Allen
Corresponding tool: Allen wrench
Features: strong torque, suitable for hidden installation
Application scenarios: mechanical equipment, furniture (such as IKEA), bicycle parts
Hex head
Corresponding tool: wrench or socket
Features: easy installation, can apply large torque
Application scenarios: building structures, mechanical equipment
Torx
Corresponding tool: Torx Screwdriver
Features: Better anti-slip performance, suitable for high torque
Application scenarios: automotive manufacturing, electronic products, high-end equipment
Square slot (Robertson)
Corresponding tool: square head screwdriver
Features: not easy to slip, high construction efficiency
Application scenarios: woodworking industry, more common in Canada
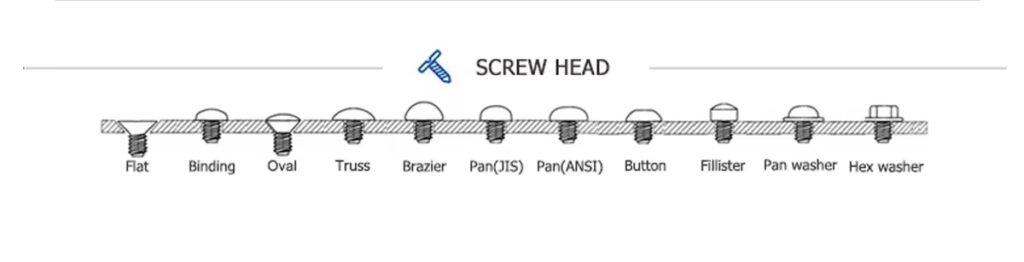
Next we need to understand the head shape of the screw
Common screw head types and their characteristics and applications
1.Pan Head
Features: Slightly convex on the top, with rounded edges
Advantages: Beautiful appearance, suitable for exposed installation
Applications: Electronic products, small appliances, toys, etc.
2.Flat Head / Countersunk
Features: The head is flat and can be flush with the surface of the material
Advantages: No protrusion after installation, improving aesthetics
Applications: Furniture, doors and windows, hardware, etc.
3.Oval Head
Features: The head is a combination of semicircle + flat
Advantages: Both beautiful and partially countersunk effects
Applications: Decorative occasions, such as exposed parts of furniture
4.Button Head
Features: The head is large and hemispherical
Advantages: Large contact surface, suitable for load-bearing or tightening without loosening
Applications: Mechanical assembly, bicycles, skateboards, etc.
5.Hex Head
Features: Hexagonal convex head shape
Advantages: Using a wrench or socket tool, it is easy to apply large torque
Applications: Mechanical structure, building assembly, engineering projects, etc.
6.Socket Head Cap Screw
Features: small head, hexagonal hole inside
Advantages: suitable for assembly with limited space
Applications: mechanical equipment, mold installation, precision parts
7.Flange Head
Features: head with a washer-shaped flange
Advantages: increase contact surface, reduce looseness
Applications: automotive parts, heavy equipment
Then we need to understand the surface treatment of the screws
Surface treatment is the key link that determines the quality and durability of screws. Different surface treatment methods can improve the corrosion resistance, aesthetics, wear resistance of screws, and even affect their conductivity.
Common screw surface treatment methods (Finishing) and their characteristics:
1.Electrogalvanized (Zinc Plated / Electro Galvanized)
Appearance: silvery white or bluish white
Features: general anti-corrosion performance, low cost
Application: indoor use, such as furniture, electronic equipment
2.Hot-dip galvanized (Hot-dip Galvanized)
Appearance: grayish white, thicker coating
Features: strong anti-rust ability, suitable for outdoor or humid environment
Application: building steel structure, outdoor facilities, bridges, etc.
3.Dacromet
Appearance: silver gray or bright silver
Features: high temperature resistance, super strong anti-corrosion, environmentally friendly and chromium-free
Application: automotive parts, wind power equipment, heavy industry
4.Black Zinc (Black Zinc)
Appearance: black or grayish black
Features: has certain anti-corrosion, visual beauty
Application: electronic products, mechanical equipment, parts with high appearance requirements
5.Phosphating (Phosphating)
Appearance: dark gray or black gray
Features: general anti-rust ability, but good adhesion with coating
Application: pre-painting treatment, military industry, machinery industry
6.Oxidation black (Black Zinc) Oxide
Appearance: black
Features: weak rust resistance, but high aesthetics and good wear resistance
Applications: tool parts, instruments, light industrial parts
7.Nickel Plated
Appearance: bright silver-white
Features: strong decorative effect, medium corrosion resistance
Applications: high-end decorative parts, electrical contact surfaces
8.Chrome Plated
Appearance: extremely bright
Features: anti-oxidation, beautiful and wear-resistant
Applications: automotive parts, home hardware, decorative occasions

So we can understand the types of screws
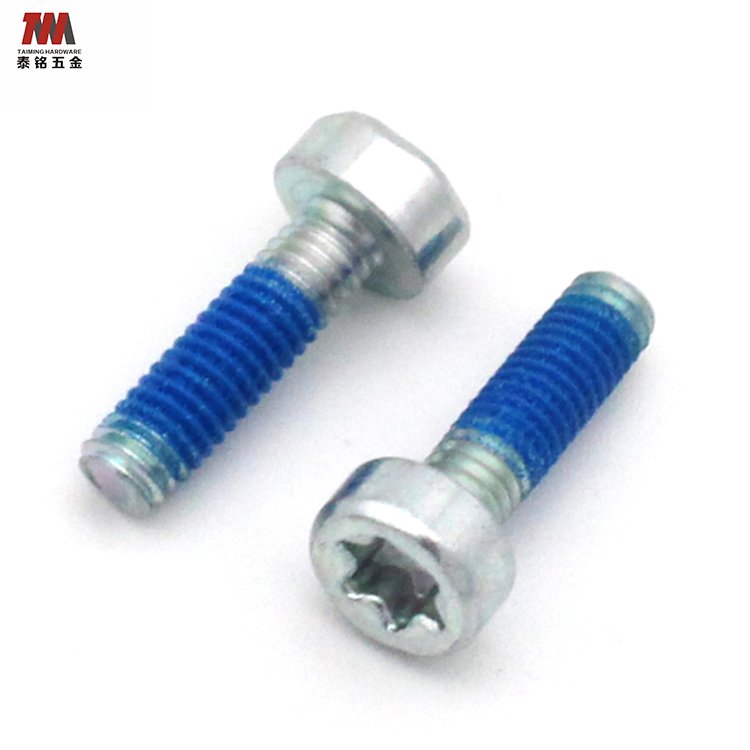

1.Nylon Patch Screw
A nylon patch is a pre-applied thread locking feature commonly used in screws and bolts. It consists of a tough nylon material that is initially applied as a dry powder, then melted and fused into the threads through heat. Unlike full 360° coatings, nylon patches are usually applied on just one side of the threads.
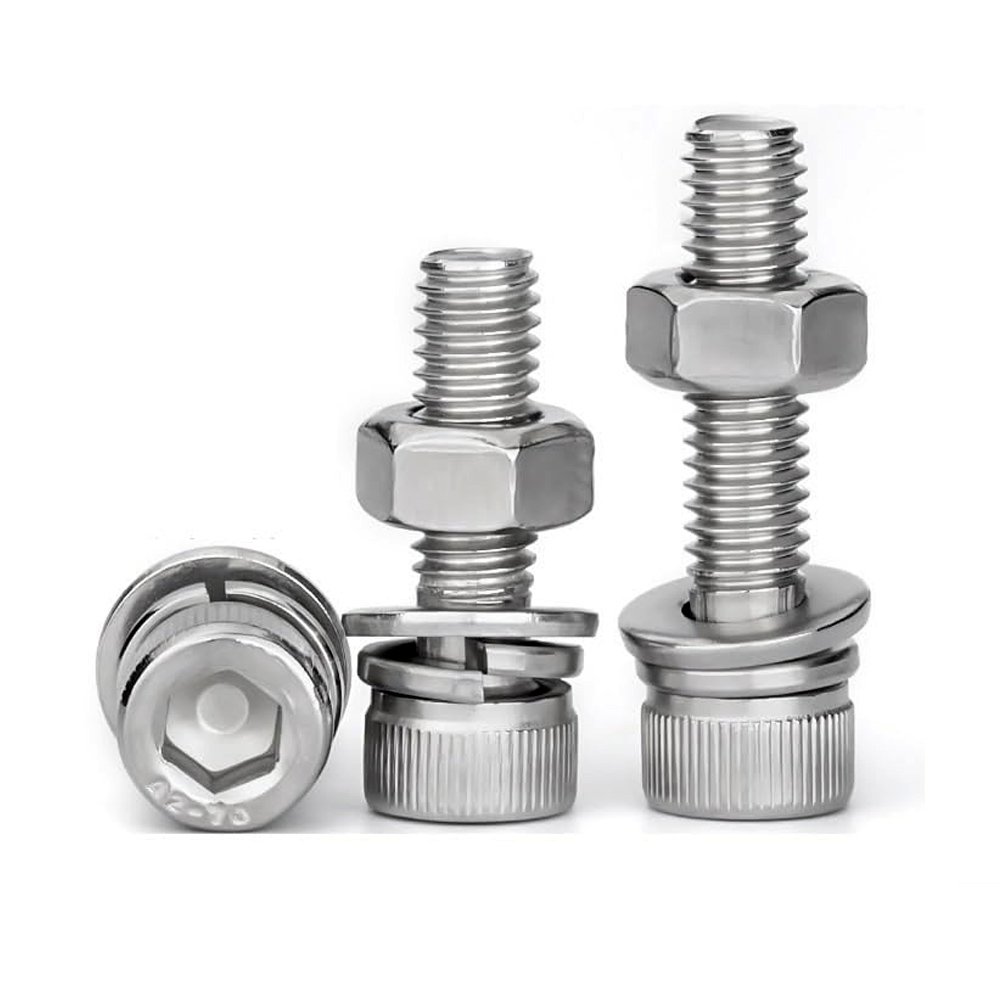

2.Combination Screw
A combination screw refers to a fastener that integrates a screw with additional components such as a spring washer, a flat washer, or a toothed lock washer, which are pre-assembled into a single unit.
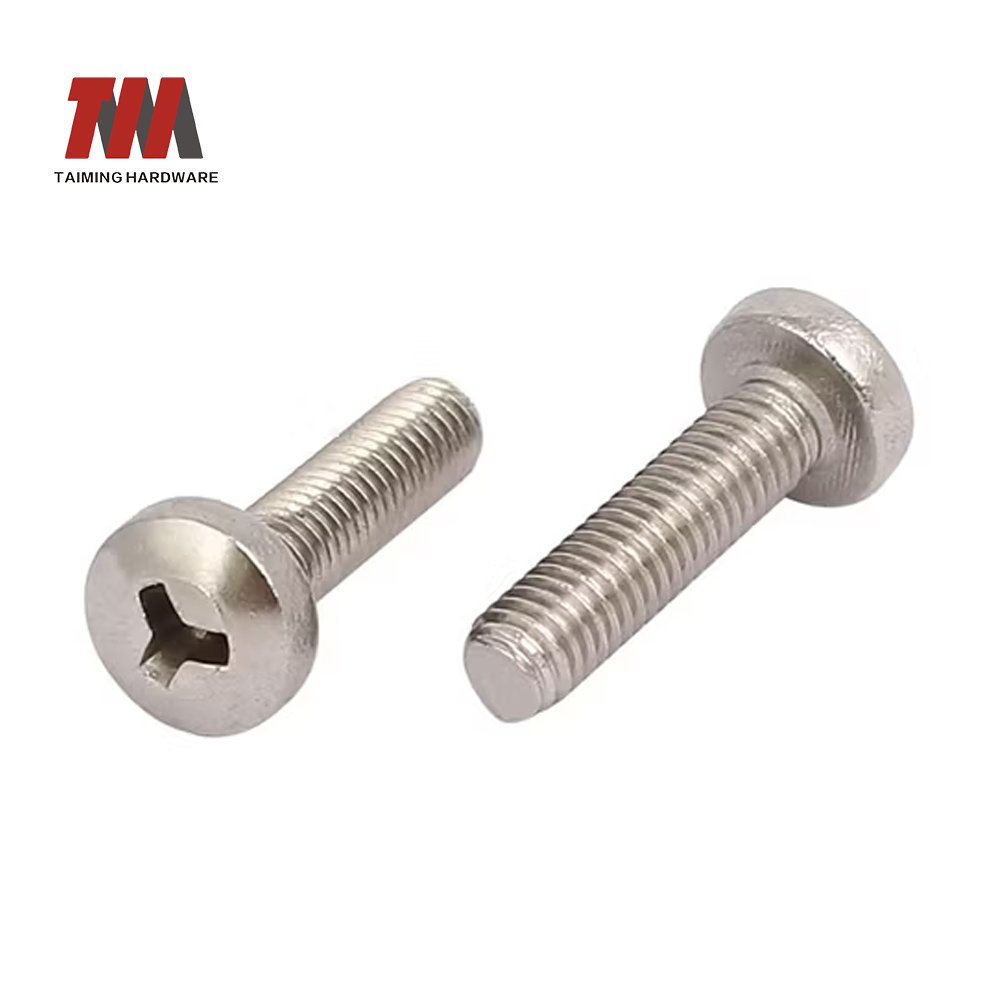

3.Machine Screws
Machine Screws are fasteners used in mechanical equipment and precision assembly. They are fully threaded and usually require nuts or prefabricated threaded holes. They do not have self-tapping capabilities.
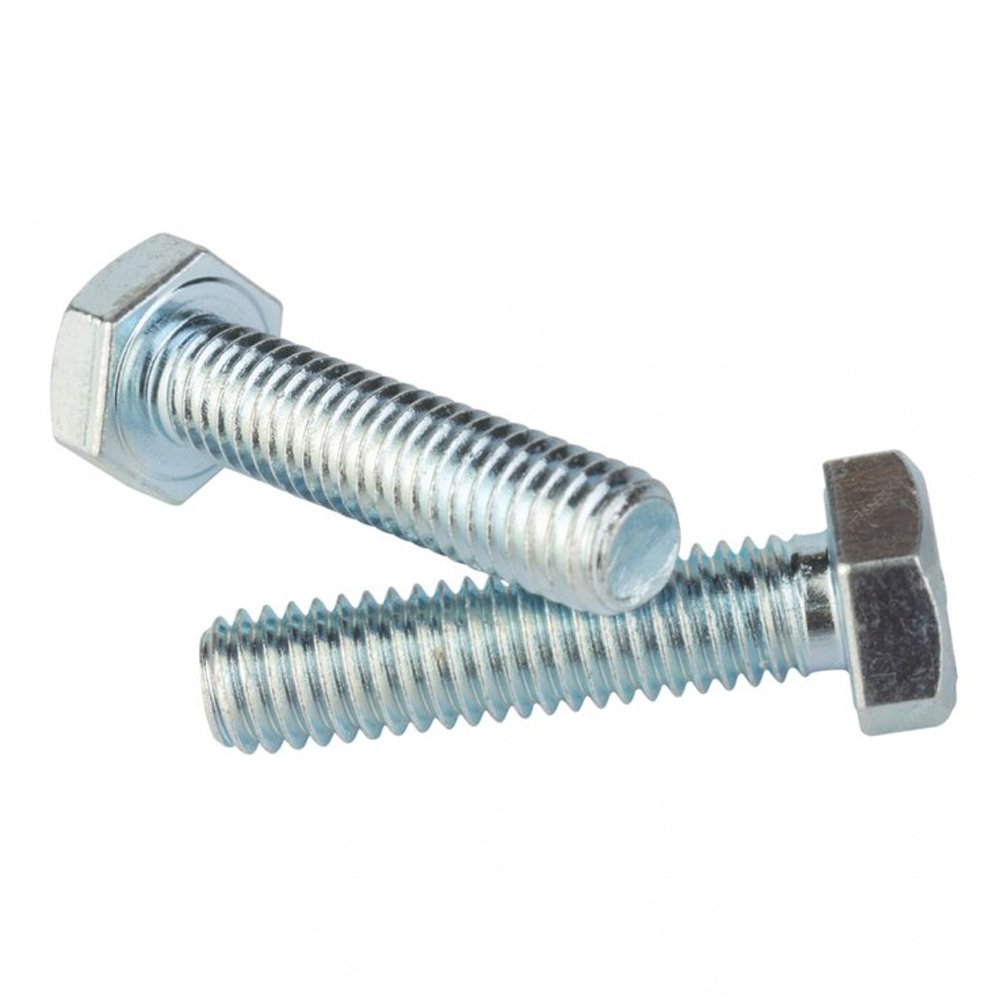

4.External Hexagon Screws
External Hexagon Screws(lag bolts) are fasteners with an external hexagonal head. They need to be installed with a wrench (such as an open-end wrench, a plum wrench, or a socket). They are widely used in high-torque, high-strength fastening scenarios.
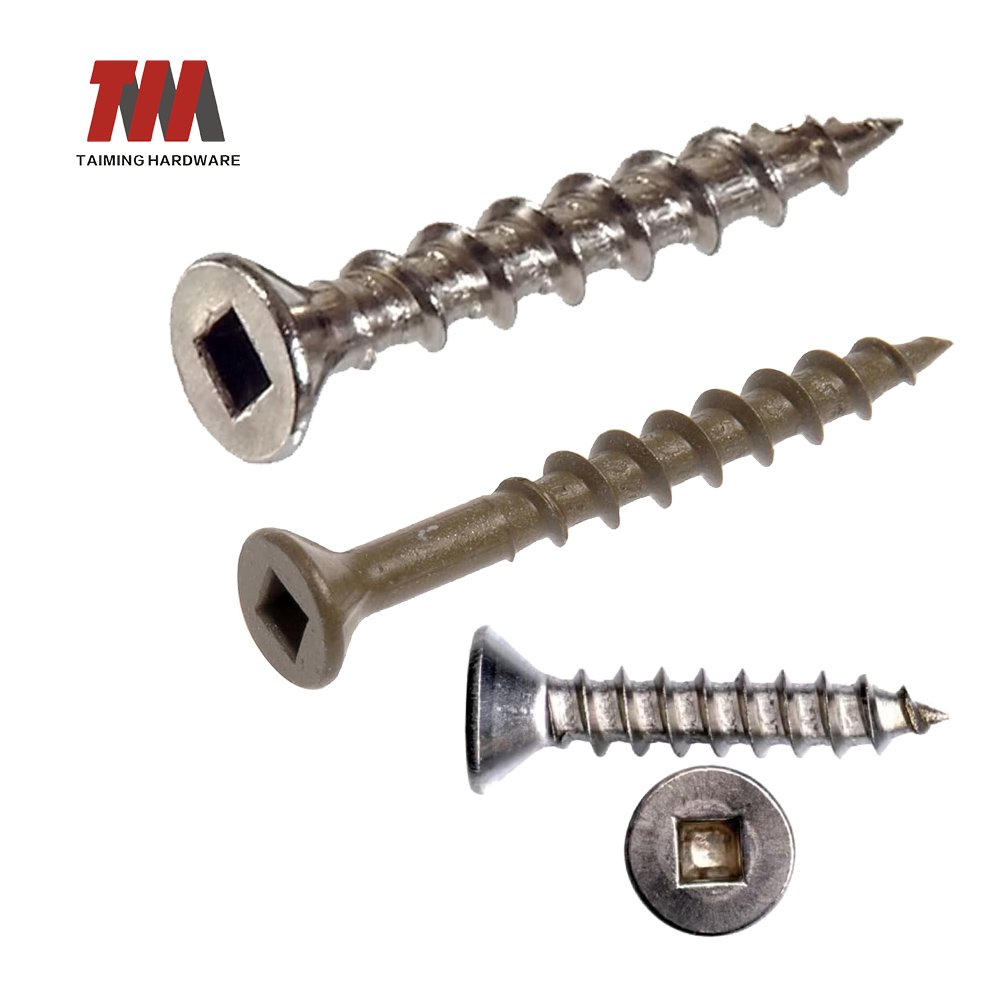

5.Tapping Screw
Tapping Screw is a fastener that can be screwed directly into the material and form threads by itself without pre-processing the threads. It is widely used in rapid assembly and specific material connection.strength fastening scenarios.
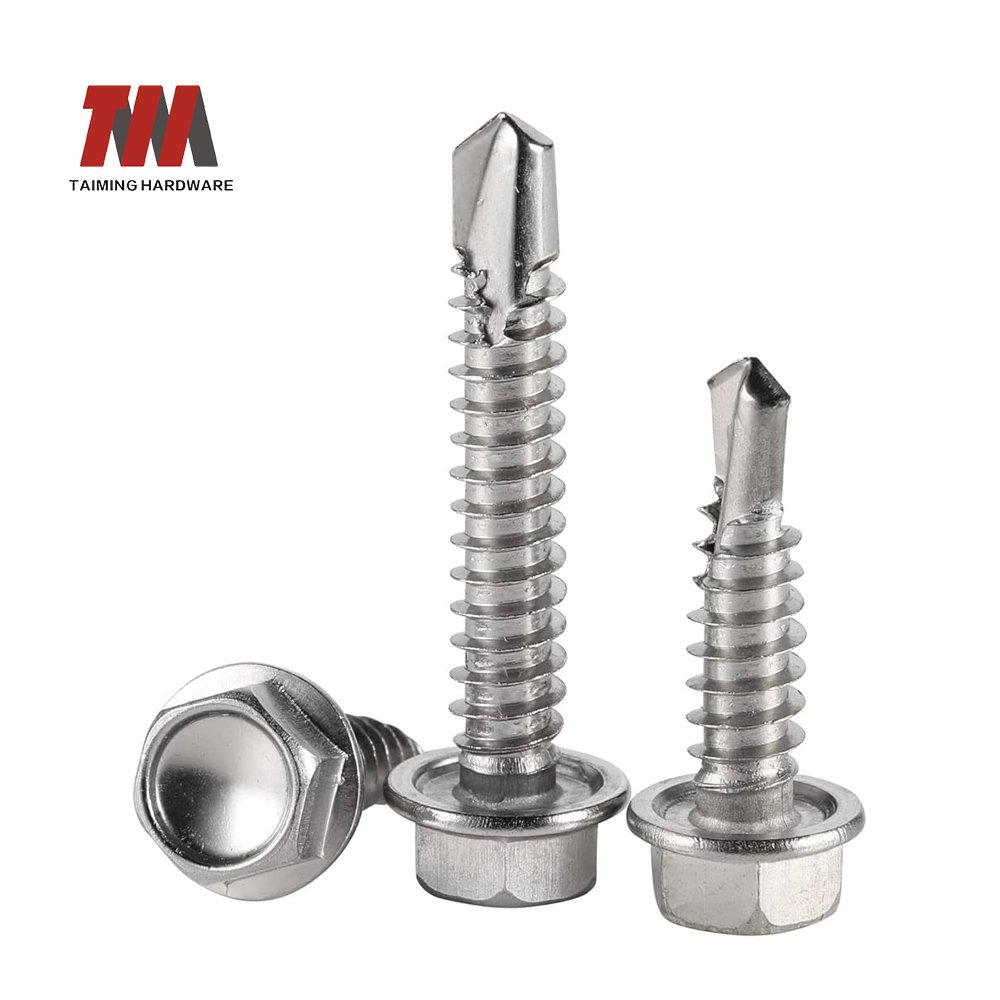

6.Drilling Screws
Drilling Screws (self-drilling screws/self-drilling screws) are fasteners with built-in drill tips that can penetrate materials and form threads simultaneously without pre-drilling. They are suitable for scenes such as metal plates and light steel structures.
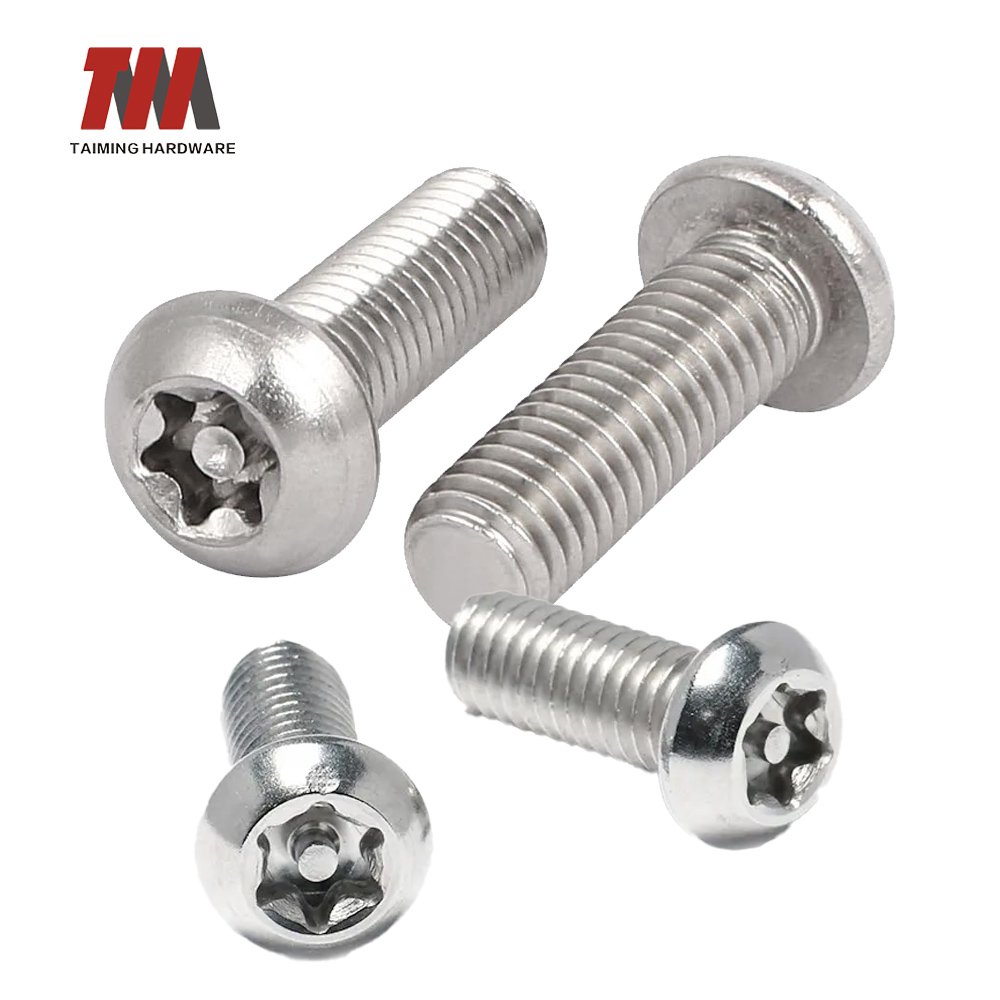

7.Security Screws
Security screws feature special heads that make them both significantly harder to remove and more resistant to pressure or wear. Typically made from steel with a zinc coating, security screws are also known as tamper-proof, anti-tamper, and anti-theft screws.
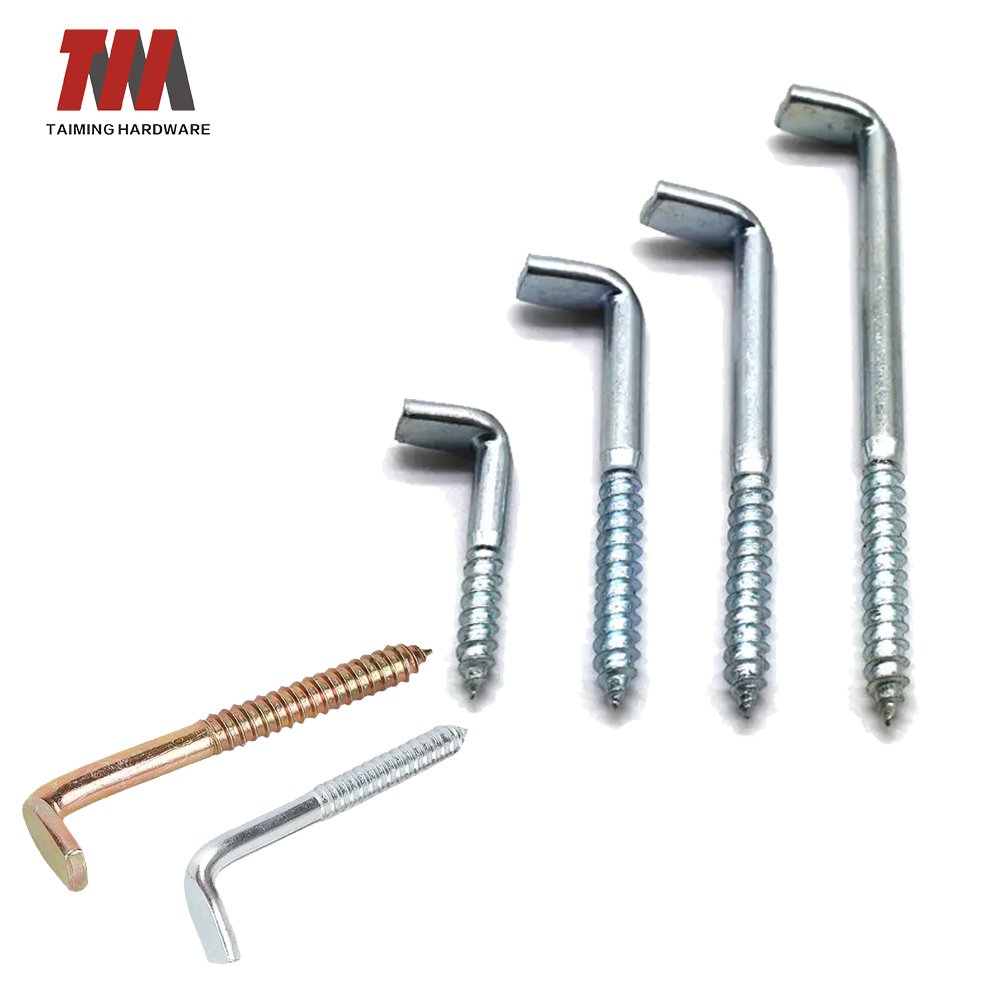

8.L Shape Screws
L Shape Screws are a type of fastener with a unique L-shaped structure. According to the design differences, they are mainly divided into two types: L-shaped anchor bolts and L-shaped handle screws. They are suitable for fixing and adjusting needs in different scenarios.
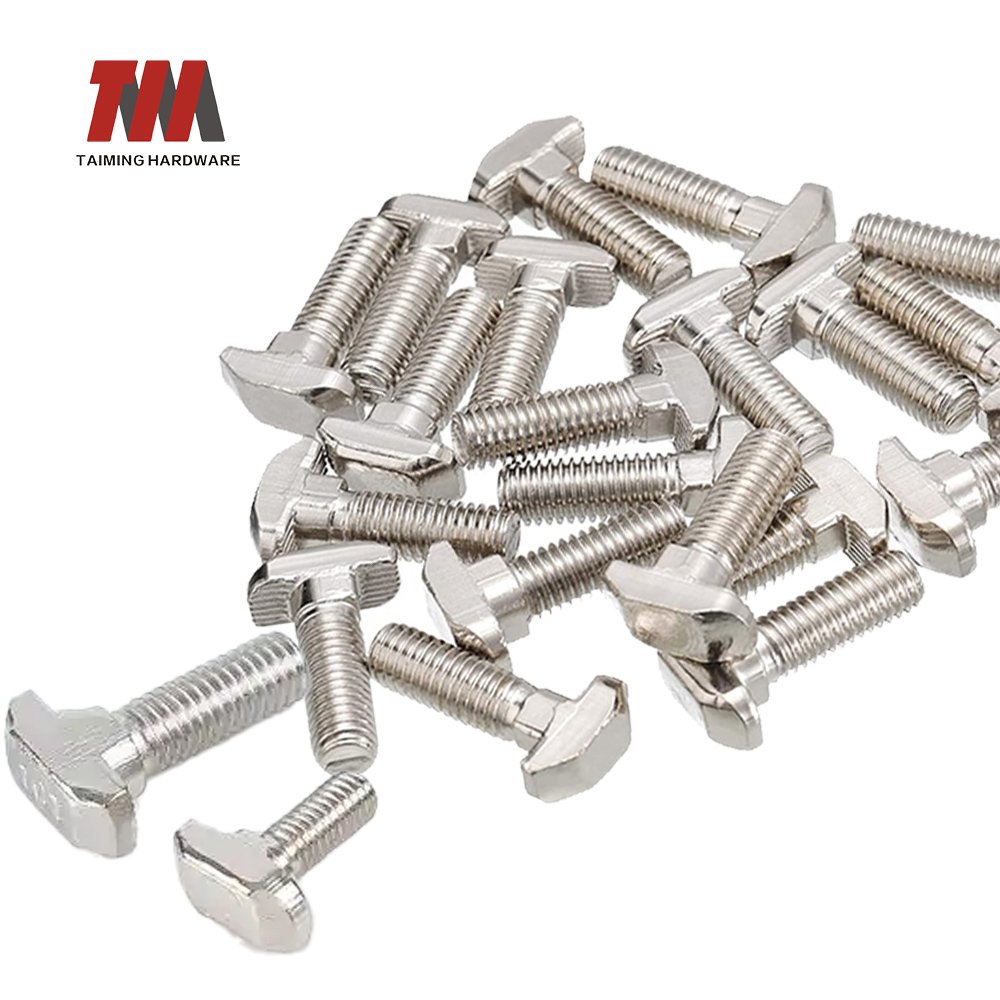

9.T Shape Screws
T Shape Screws are a type of fastener with a “T”-shaped head or overall structure. According to design differences, they are mainly divided into T-Slot Bolts and T-Handle Screws, which are used for mechanical fixation and manual quick adjustment scenarios respectively.
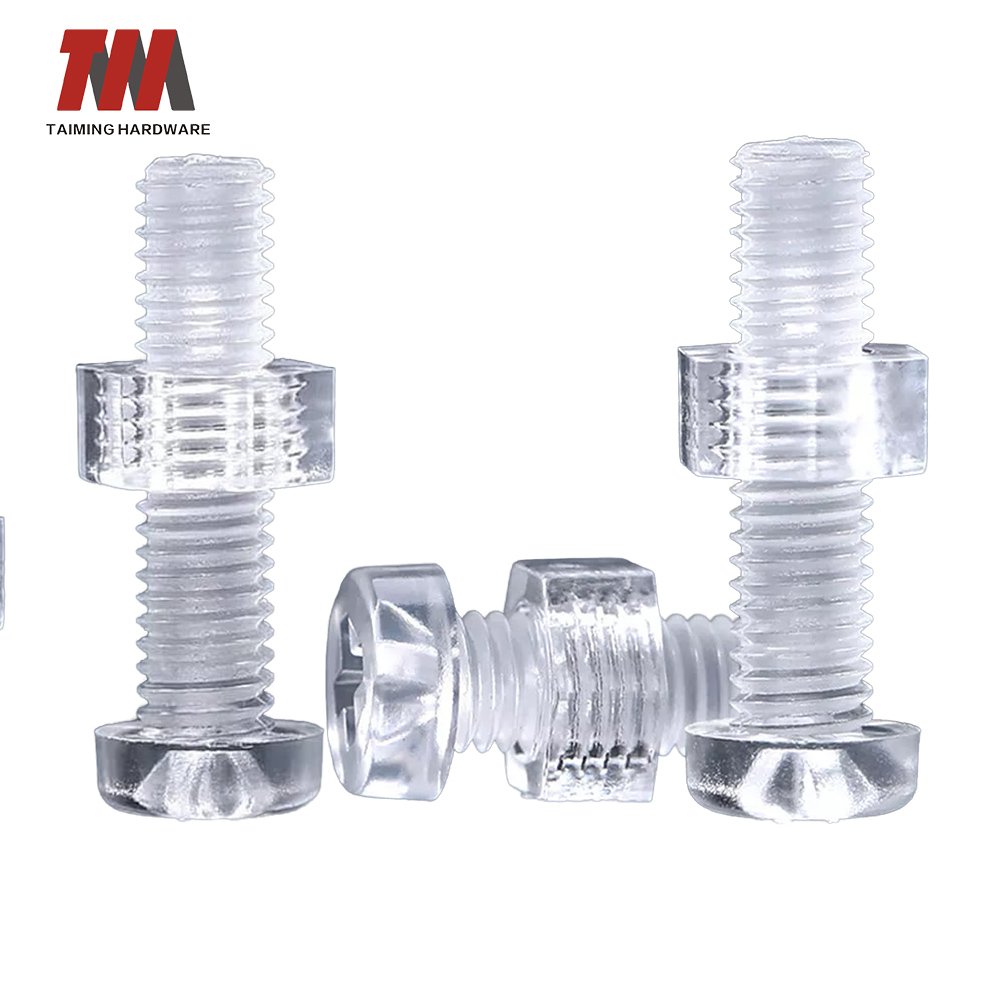

10.Plastic Screws
A plastic screw is a type of fastener made from plastic materials, typically polymers like nylon or PE (polyethylene). we mainly use PA, PP, POM and high-performance plastics such as PVDF, PTFE and PEEK to manufacture our screws.
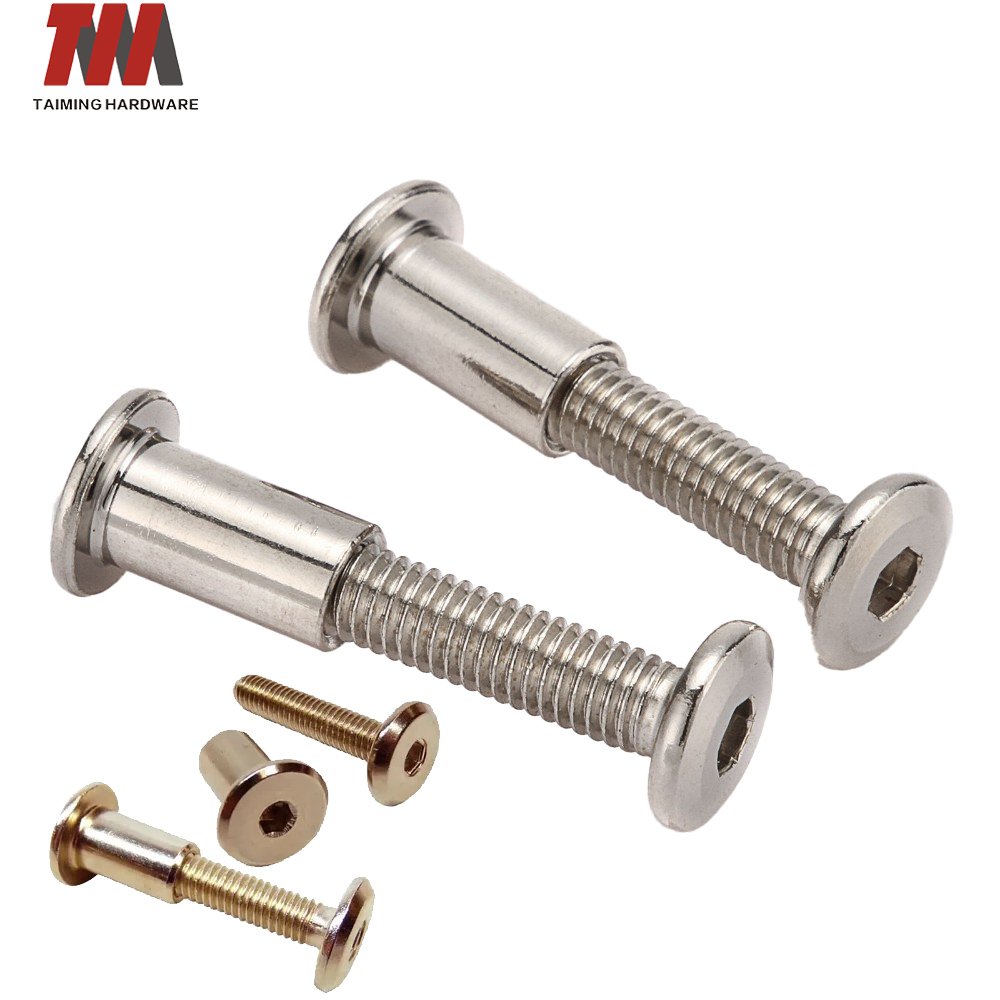

11.Connecting Screws
Connecting Screws consists of 2 parts: male sleeve and the ribbed female component. Popularly known as the sex bolt or the Tool Post Bolt, it is used to secure parallel panels together. It has multiple uses in the furniture industry.
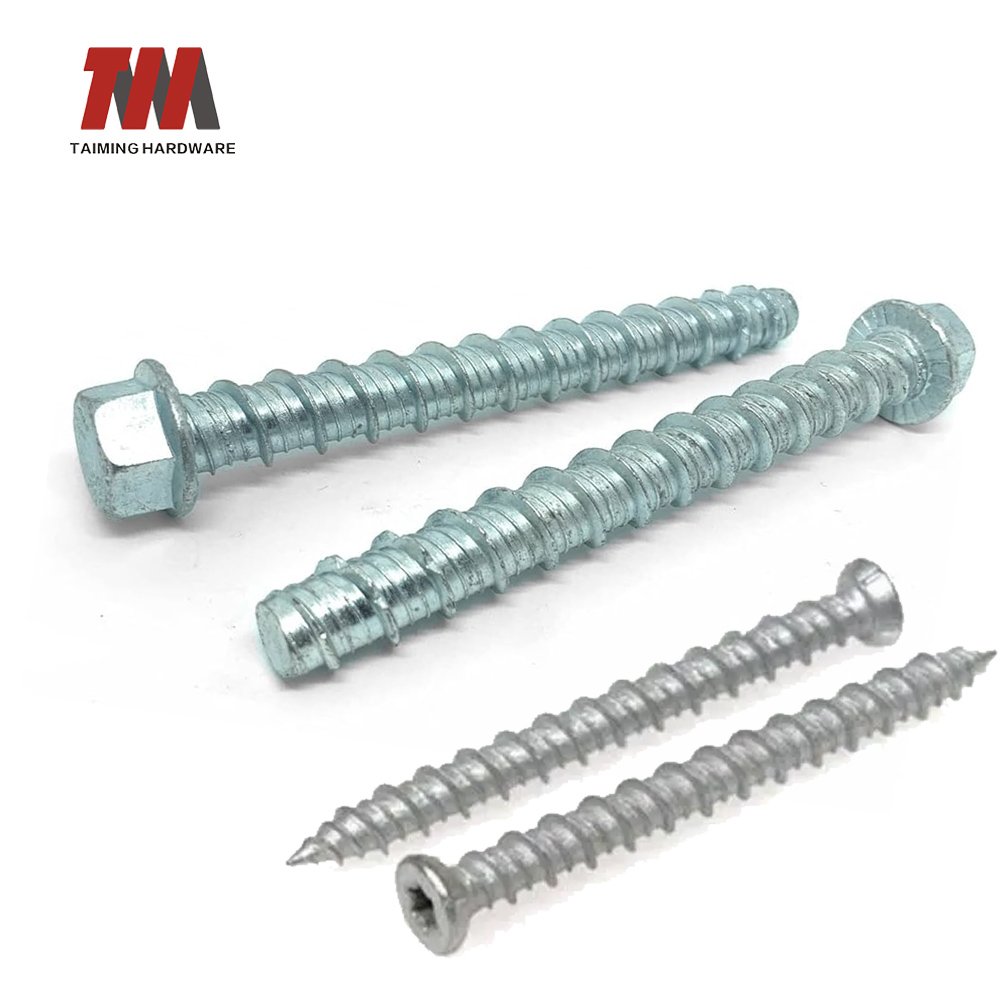

12.Concrete Screw
Concrete screws may also be called concrete anchors, concrete fasteners, or in the USA they are often called by the brand name Tapcon screws. Concrete screws are a quick and easy way of fastening to concrete, they do not require hammering like other fasteners.They have high-low threads, where the high thread is sharp and deeply cut to allow for maximum holding power in the base material, while the low thread provides stability.
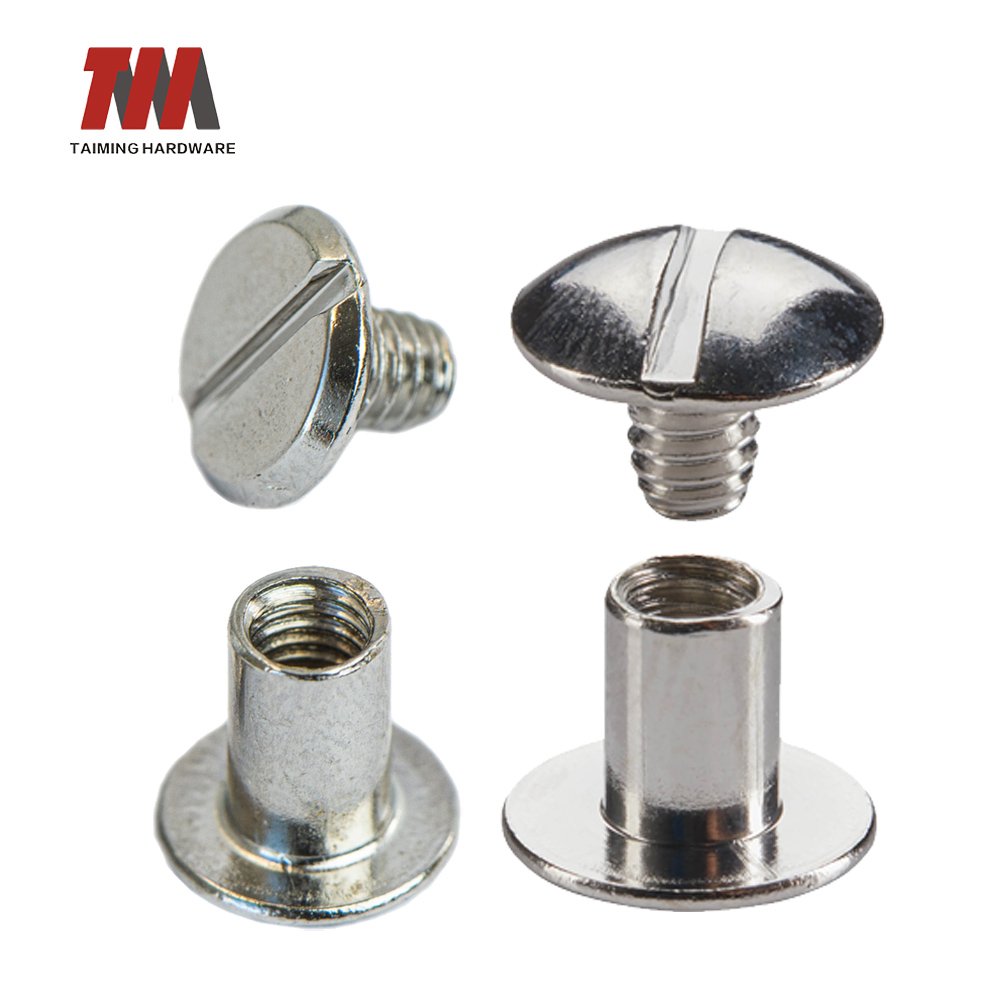

13.Chicago Screws
A Chicago Screw is a two-part component consisting of a screw and a post used to bind materials together, similar to a double-capped rivet, except that the connection is not permanently set and can be unscrewed and reused. Typically made from brass, steel, or aluminum
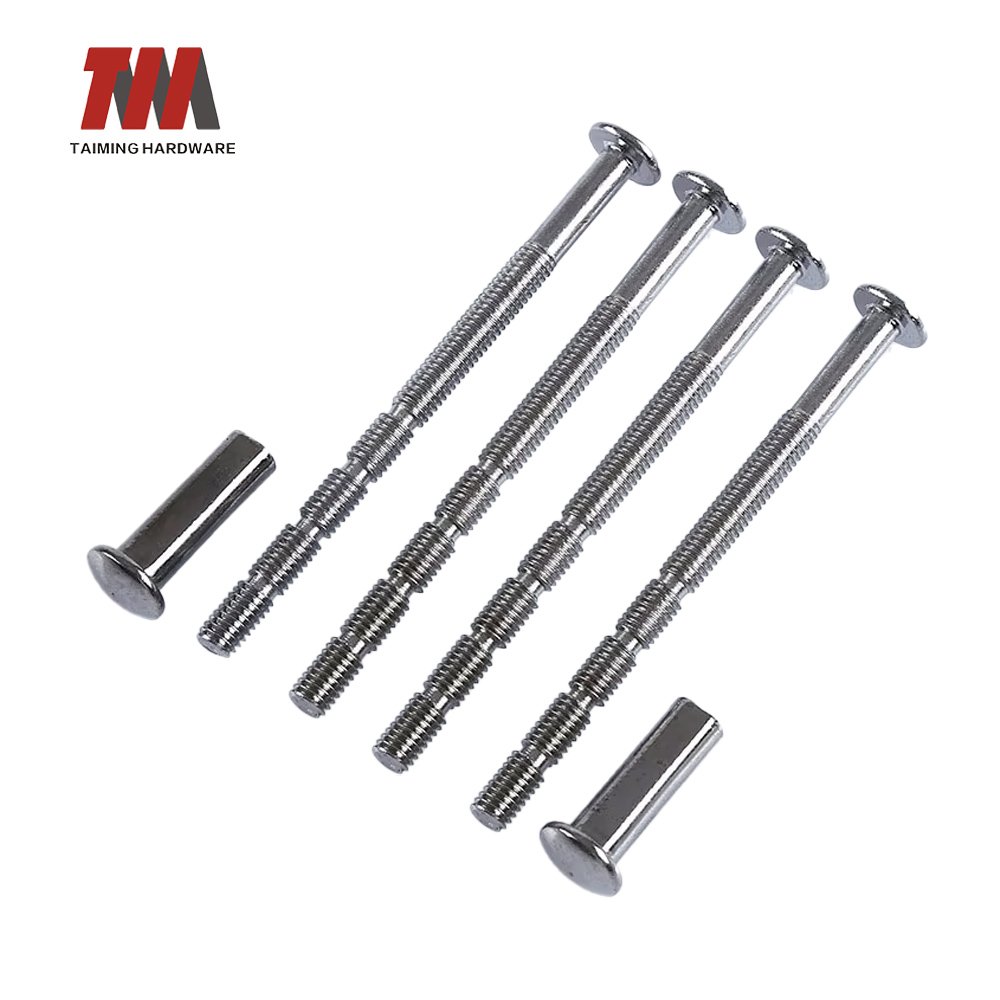

14.Bamboo Screws
Bamboo screws refer to a type of connecting screws used primarily in door handle assemblies. These screws are characterized by their unique “bamboo-shaped” design, which is alternating ridges and grooves along the screw shaft, similar to the shape of a bamboo joint.
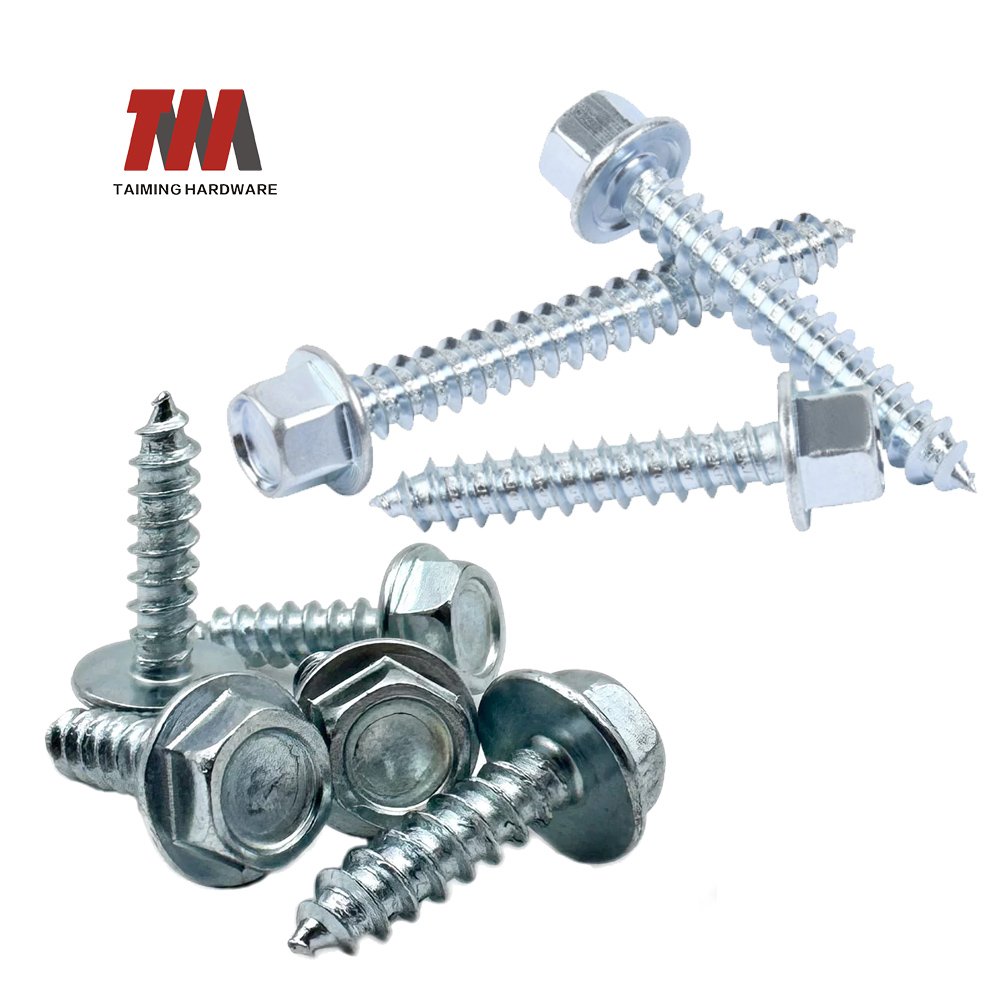

15.Flange Head Screw
A flanged head can be any head style (except the countersunk screws) with the addition of an integrated flange at the base of the head. This eliminates the need for a flat washer.
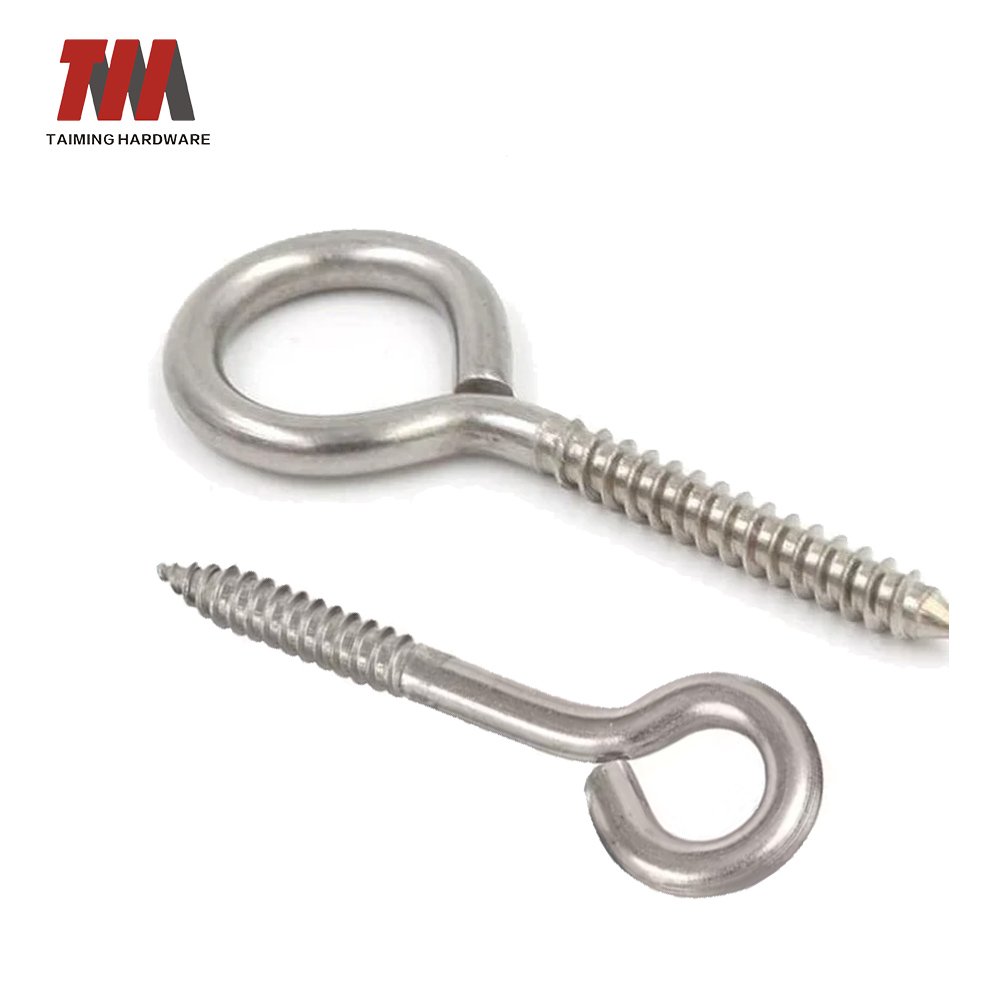

16.Eye Screws
Eye screws are a type of fastener featuring a threaded shank with a loop—or “eye”—at one end. They’re commonly used to create attachment points in wood, drywall, and other materials for hanging or securing items like cables, chains, picture frames, or even light fixtures.
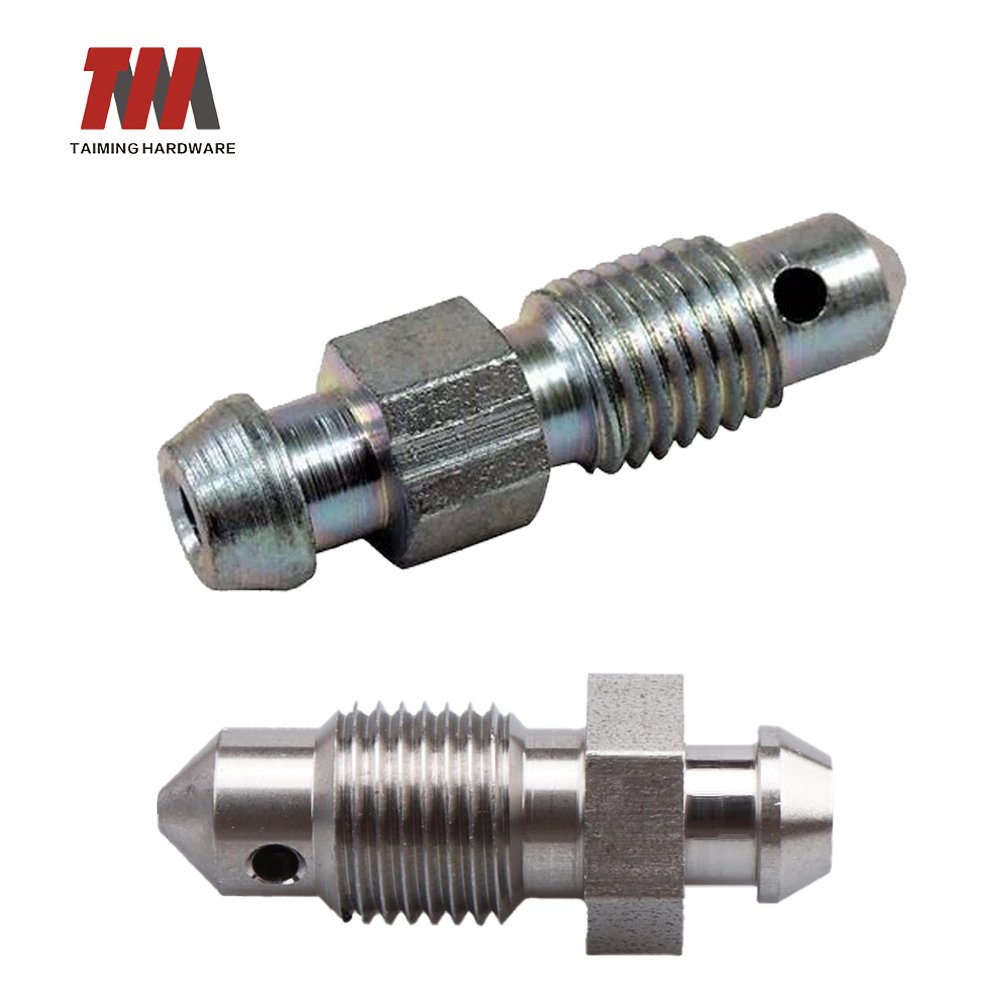

17.Bleeding Screw
On a hydraulic vehicle braking systems, the bleed screws (sometimes known as bleed nipples or bleeder valves) are located at the top of each brake caliper to allow bleeding of the braking system.
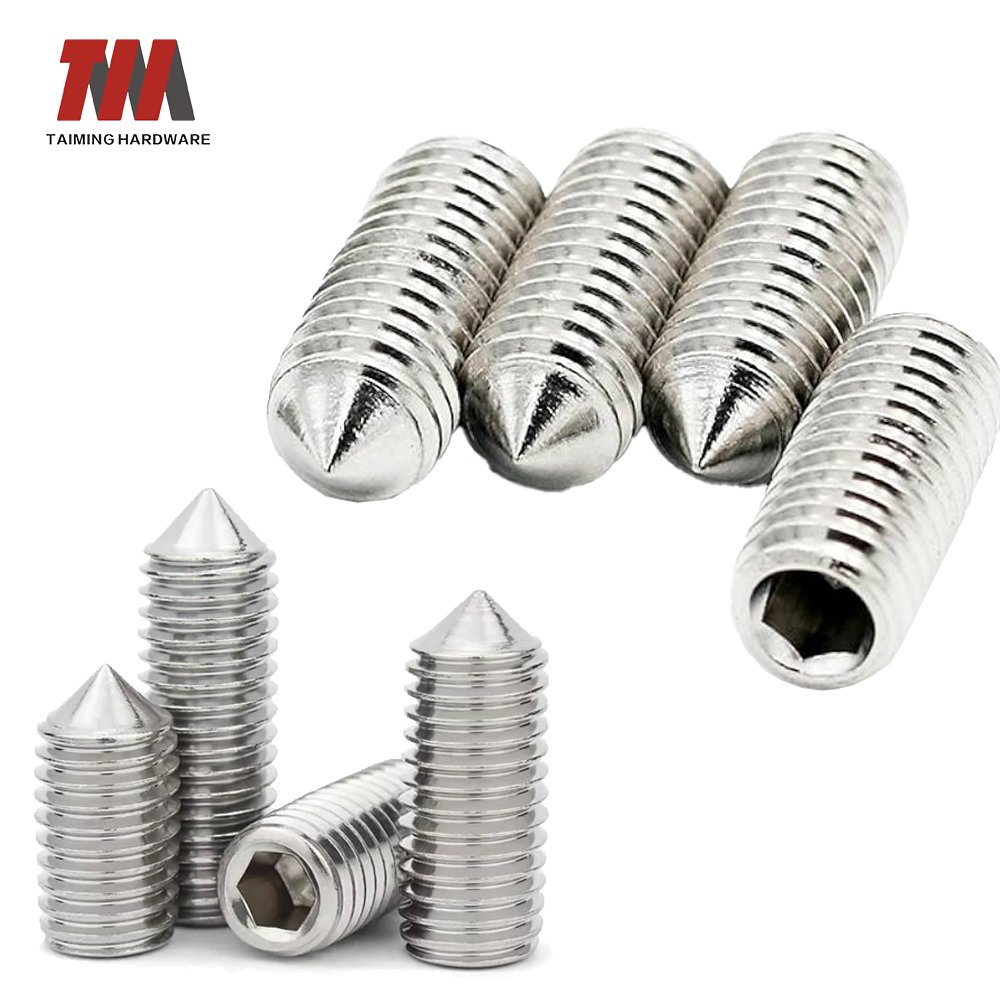

18.SetScrew
A set screw (also known as a grub screw) is a type of headless fastener designed to secure one object within or against another—without using a nut.
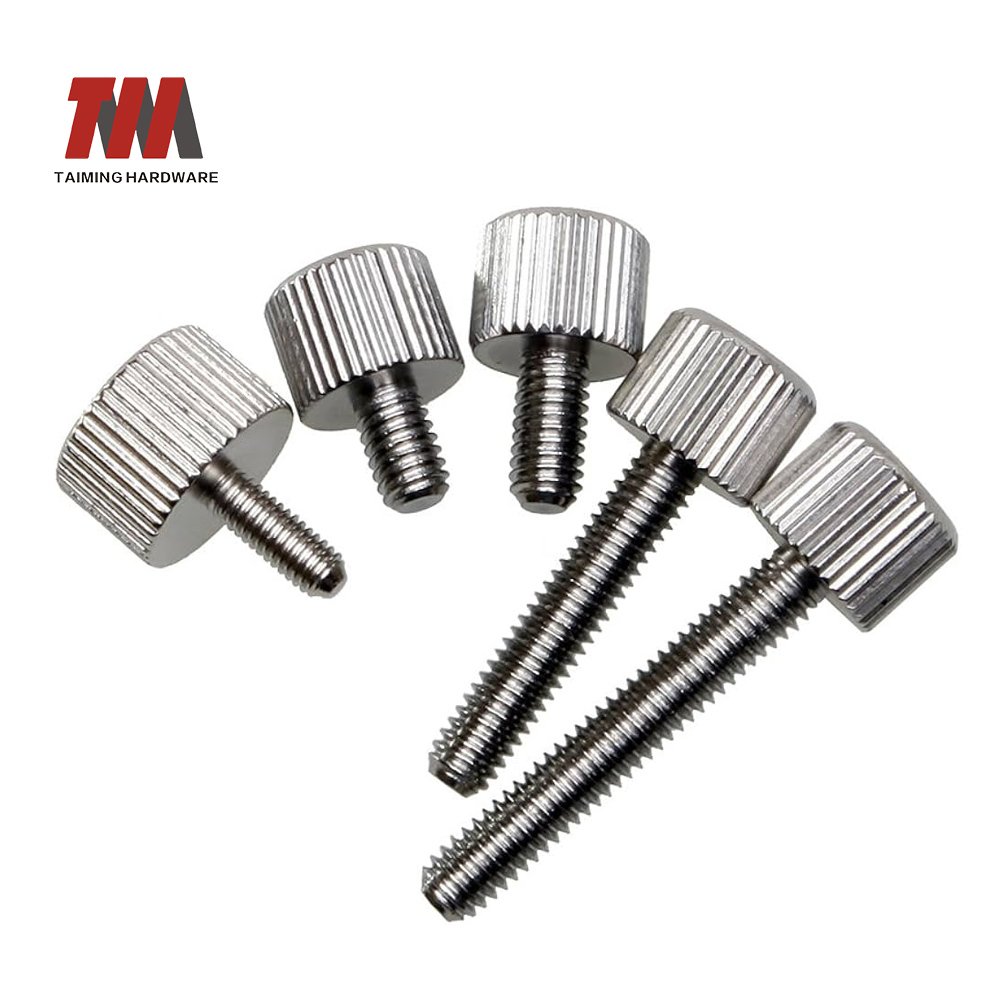

19.Thumb Screw
A thumb screw is a type of screw designed to be tightened and loosened by hand, without the need for tools. It features an enlarged, textured, or knurled head—often in a wing, knob, or flat-head shape—that provides grip for manual operation.
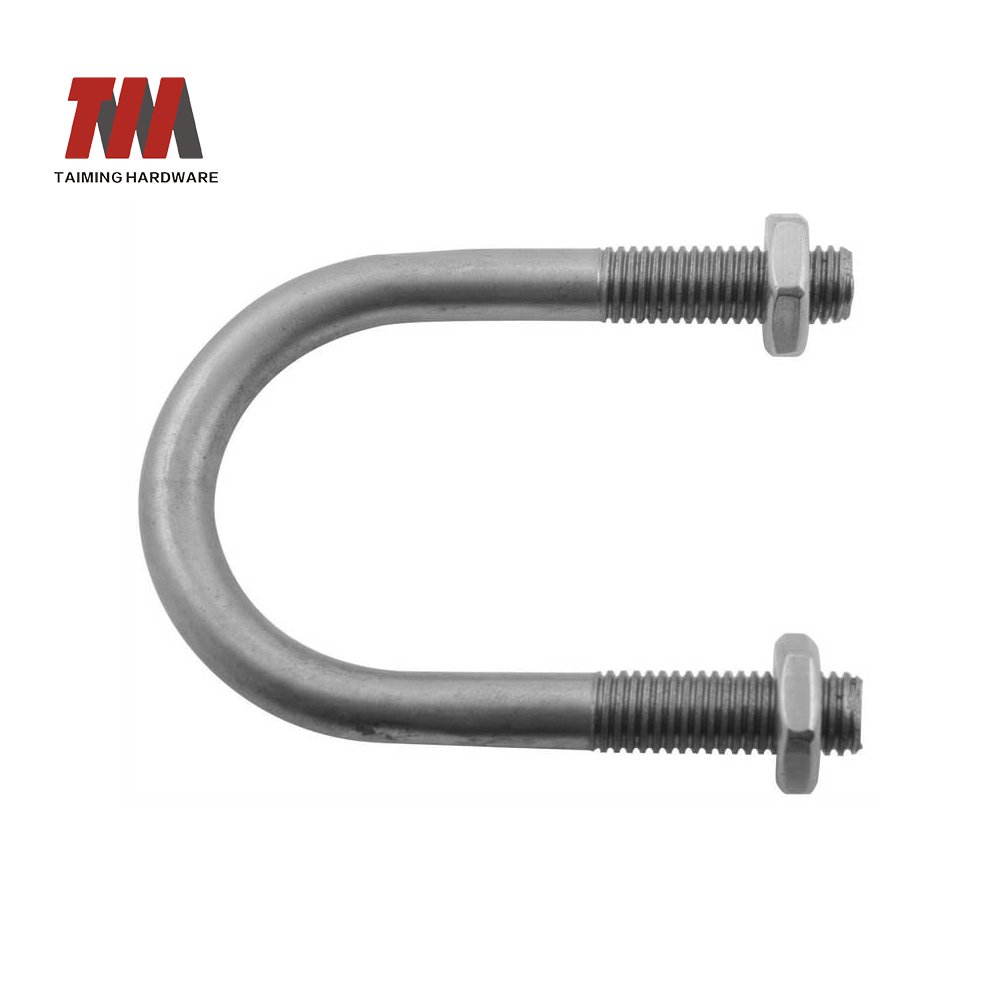

20.U Bolts
A U-bolt is a type of fastener shaped like the letter “U”, with two threaded arms or legs extending from a curved base. It’s primarily used to secure pipes, tubes, or round objects to flat surfaces or to hold components together in mechanical assemblies.
